

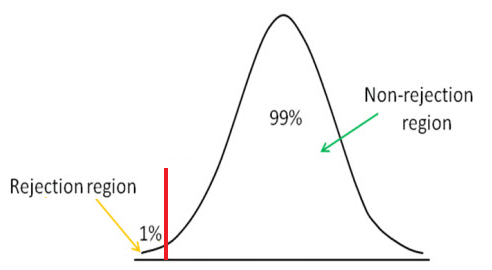
This is also called a Type I error (choosing Ha when Ho is actually correct). The alpha value is the percentage chance that you will reject the null (choose to go with your Ha research hypothesis as you conclusion) when in fact the Ho really true (and your research Ha should not be selected). To do this, you must first select an alpha value. Step 4: Using the z-table, determine the rejection regions for you z-test. So, the z-test result, also called the test statistic is 1.825. This Site has several examples under the Stats Apps link.
However, there are many applications that run such tests.
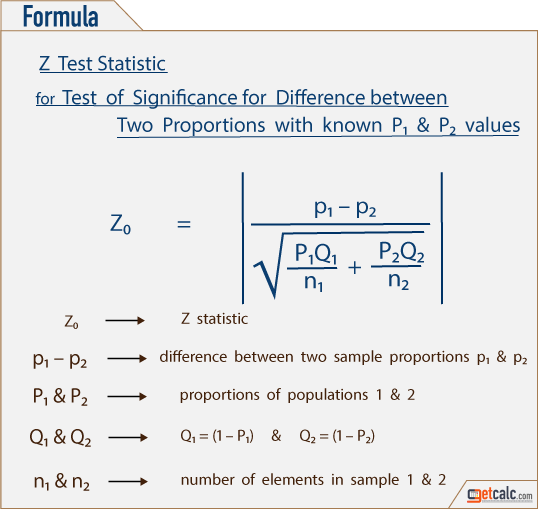
In this example, we are using the z-test and are doing this by hand. NOTICE2: The Ho is the null hypothesis and so always contains the equal sign as it is the case for which there is no significant difference between the two groups. In a two-tailed test, the Ha contains a NOT EQUAL and the test will see if there is a significant difference (greater or smaller). NOTICE1: The Ha in this example is TWO-TAILED because we are interested in seeing if Michigan is significantly different than the population mean. Ha: mean per student per year funding for Michigan ≠ mean per student per year funding for the USA This can also be written as the following. Ho: mean per student per year funding for Michigan = mean per student per year funding for the USA NOTE: There are many ways to write out Ho. Hypothesis: The mean per student per year funding in Michigan is significantly different than the average per student per year funding over the entire USA. If you do not have this information, it is sometimes best to use the t-test. To run a z-test, it is generally expected that you have a larger sample size (30 or more) and that you have information about the population mean and standard deviation. Using the dataset, you would need to first calculate the sample mean. NOTE: This entire example works the same way if you have a dataset. Use the z-test and the correct Ho and Ha to run a hypothesis test to determine if Michigan receives a significantly different amount of funding for public school education (per student per year). Next, suppose you collect a sample (n = 100) from Michigan and determine that the sample mean for Michigan (per student per year) is $6873 You know that the USA mean public school yearly funding is $6800 per student per year, with a standard deviation of $400. Suppose it is up to you to determine if a certain state (Michigan) receives a significantly different amount of public school funding (per student) than the USA average. Running a Two-Tailed z-test Hypothesis Test by Hand


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
